Storage Components
Storage Components.Floppy Drives.

- A Floppy Disk Drive (FDD) magnetically reads and writes information onto floppy diskettes, which are a form of removable storage media.
- The main drawback to the floppy diskette is that it only holds 1.44 MB of information, although most PCs still have a floppy drive.
The Hard Drive.
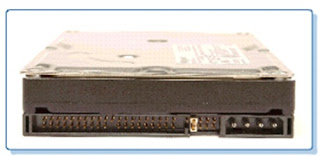
- The HDD has a much larger storage capacity than the floppy for long-term storage.
- It stores programs and files, as well as the operating system.
- Typically, the HDD is an internal drive that cannot be removed from the computer.

- Hard Drive Components include: disk platters, read/write heads, head actuator assembly, spindle motor, logic/circuit board, bezel/faceplate, configuration jumpers, and interface connectors.

- Disk platters are the actual media on which data is stored in the hard disk drive.
- A hard disk drive typically has two to ten platters. They are usually either 2 ½” or 3 ½” in diameter and are typically constructed of aluminum or a glass-ceramic composite material.
- Platters are stacked with spaces between them on a hub that holds them in position, separate from one another.
- The hub is also called the spindle.
- The hard disk drive functions in much the same way as a floppy disk drive.
- The disk platters spin at a high speed while the drive heads access the media to conduct read or write operations.
- Personal computers have at least one HDD installed inside the system unit.
- If more storage capacity is needed, another HDD can usually be added.
- The capacity of the HDD is a measure of how much information it can store.
CD-ROMs.
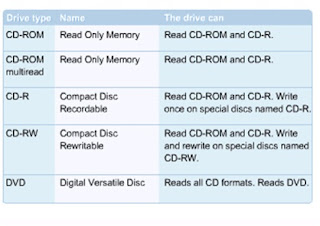
- A CD-ROM drive is a secondary storage device that reads information stored on a compact disc. The CD-ROM is an optical media.
- They are used for installing programs, running applications that install some of the files to the hard drive, and executing the program by transferring the data from the CD-ROM to memory while the program is running
- The major components within a CD-ROM drive are the optical head assembly, head actuator mechanism, spindle motor, loading mechanism, connectors and jumpers, and logic board.
- Data is stored in the form of indentations and bumps on the reflective surface of every CD-ROM disk.
- The indentations are called pits, and the bumps are called lands.
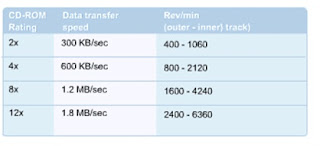
- The most important specification for a CD-ROM drive is its speed, or how fast the disc will spin. The faster the disc spins, the faster the data can be transferred to the computer’s memory.
- Two other important specifications to consider are the access time and data transfer rate.

- The DVD looks like a CD, but the storage capacity is significantly higher.
- For this reason, many software manufacturers are starting to put programs, manuals, and other documentation on one DVD instead of multiple CDs.
- Recordable DVD drives will become standard on computer systems just like the CD drive did.
Backup Hardware.

- Tape drives are most commonly used as the device for data backup on a network server disk drive. There are a variety of tape devices that use different tape formats for storing data.
- New USB storage devices can easily save and access 16MB, 32MB, 64MB, 128MB, 256MB, 512MB and 1GB.






0 komentar: